ECG HMI - Complete Electrocardiographic Device
Overview
Design and realization of an integrated portable ECG device, combining cleanroom microfabrication, embedded electronics, and display interface. Multidisciplinary project covering the entire biomedical measurement chain: from sensors to real-time visualization.
Objectives
Develop a functional electrocardiogram prototype integrating:
- Custom-fabricated ECG electrodes in cleanroom
- Acquisition card for signal processing
- Display interface (OLED/LED matrix)
Technologies Used
Microfabrication
- Photolithography: Electrode structuring
- Vacuum evaporation: Ti/Au and organic layer deposition
- PEDOT:PSS: Conductive polymer for impedance improvement
- Kapton (polyimide): Flexible substrate for electrodes
Electronics & Programming
- STM32: Microcontroller for signal processing
- CMSIS-DSP: Library for FIR filtering
- UART: Serial communication for visualization
- PCB fabrication (SMD components, reflow)
Characterization
- Impedance spectroscopy: Electrode performance measurement
- Ellipsometry: Layer thickness control
- Oscilloscope: ECG signal validation
System Architecture
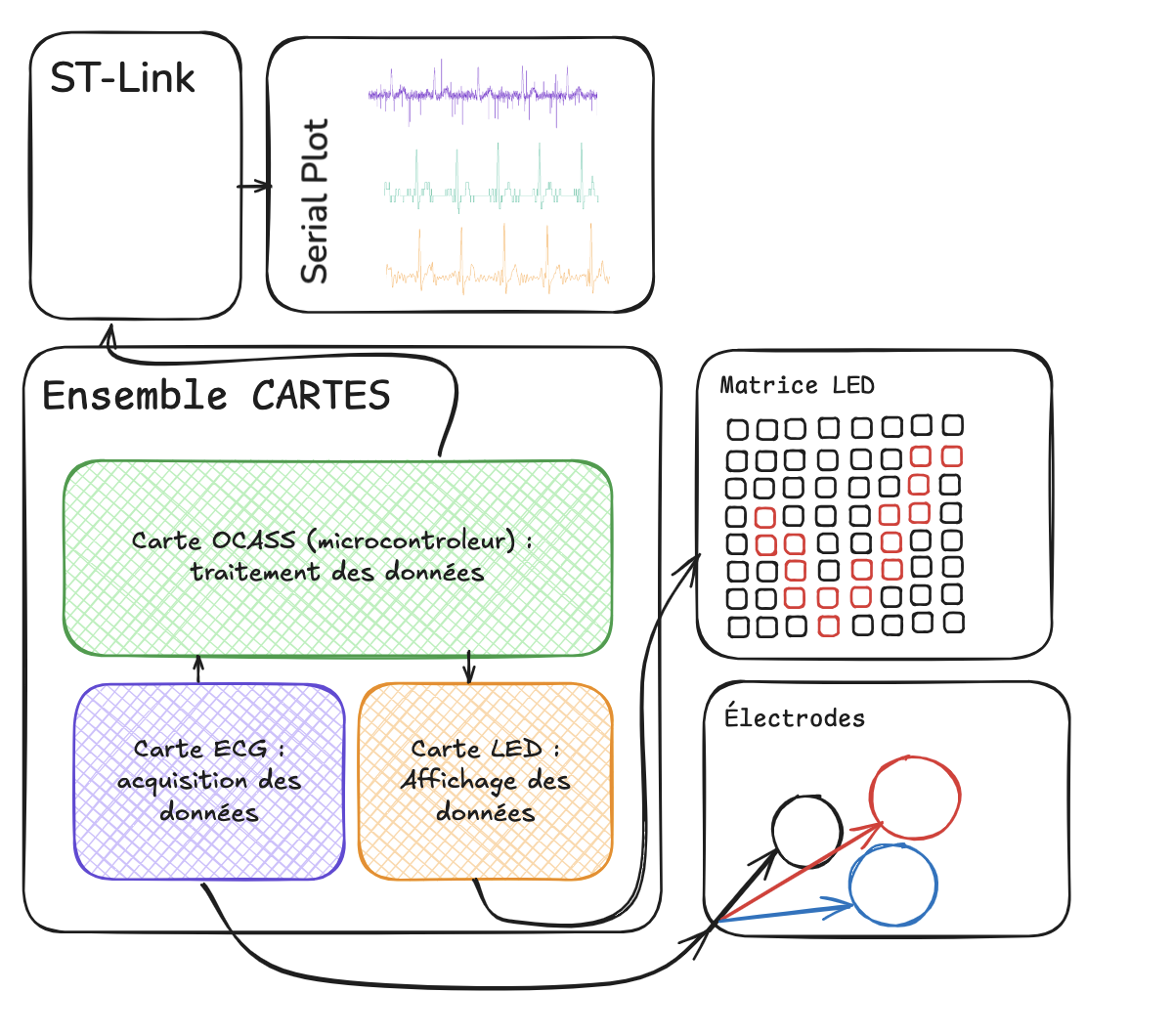
1. ECG Electrodes (Cleanroom)
Fabrication process:
- Flexible Kapton substrate
- O₂ plasma treatment for activation
- Photolithography (S1813 photoresist)
- Ti/Au evaporation (100nm)
- Lift-off and cleaning
- PEDOT:PSS coating
Performance:
- Impedance ~7 Ω (comparable to commercial electrodes)
- Water-only operation (no conductive gel)
- Nyquist diagram compliant
2. ECG Acquisition Card
Fabrication:
- SMD components soldered by reflow (stencil + hot plate)
- ±15V power supply
- Test points for validation
Signal processing:
- ECG signal capture via electrodes
- FIR filtering (CMSIS-DSP)
- UART transmission to Serial Plot
- Real-time visualization
3. Display Matrix
OLED attempt:
- Multilayer architecture (ITO/HTL/EML/ETL/Al)
- Thermal and co-evaporation
- Real-time thickness monitoring (Inficon)
- Nitrogen encapsulation
Alternative solution - 8×8 LED Matrix:
- Multiplexing card fabricated
- Adapted programming (eCampus library)
- Functional scrolling text display
Technical Challenges
Microfabrication
- Control of deposition uniformity
- Environmental management (oxygen, humidity)
- Lift-off process precision
Electronics
- SMD component soldering (defective vias)
- Methodical debugging of multiplexing card
- Multi-filter processing stability
OLED
- Oxygen spike during chamber opening (machine fault)
- Missing HBL layer → excessive voltages (13-20V)
- Matrix non-functional outside neutral environment
Learnings
Technical Skills
- Mastery of cleanroom techniques (photolithography, evaporation)
- Optical and electrical component characterization
- Real-time biomedical signal processing
- Electronic circuit fabrication and debugging
Methodology
- Importance of scientific rigor (impact of attention errors)
- Systematic and methodical debugging
- Adaptation to hardware constraints
- Multidisciplinary integration (chemistry, physics, electronics, computer science)
Innovation
- Development of gel-free biomedical electrodes
- Complete portable medical device architecture
- Mastery of complete chain: sensor → processing → display
